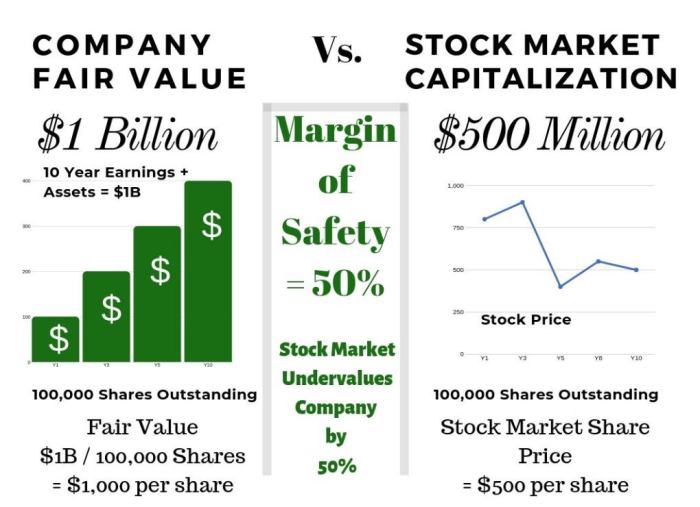
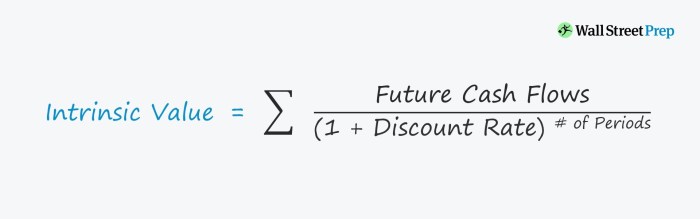The margin of safety is check all that apply – The margin of safety is a key concept in investing that helps investors identify undervalued assets and make informed investment decisions. It is a measure of the difference between the intrinsic value of an asset and its current market price.
A higher margin of safety provides a buffer against potential losses and increases the likelihood of achieving positive returns.
This comprehensive guide will explore the concept of the margin of safety, discuss different methods for calculating it, and examine the factors that can affect it. We will also provide a step-by-step process for incorporating the margin of safety into an investment strategy and discuss the limitations of this approach.
Understanding the Margin of Safety
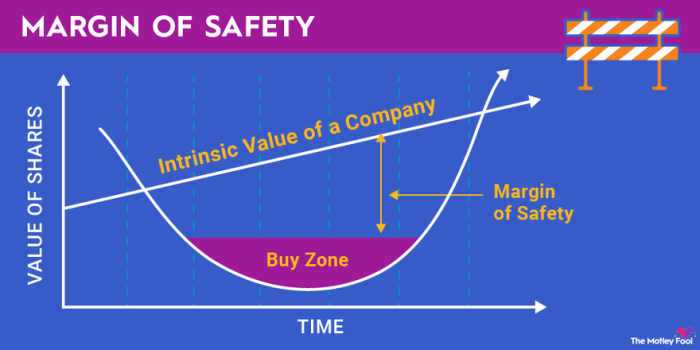
The margin of safety is a concept in investing that refers to the difference between the intrinsic value of an asset and its current market price. It provides a buffer against potential losses and helps investors make more informed decisions.
The margin of safety can be calculated using various financial metrics, such as discounted cash flow analysis, price-to-earnings ratios, and price-to-book ratios. By comparing the intrinsic value to the market price, investors can assess whether an asset is undervalued or overvalued.
Considering the margin of safety is crucial when making investment decisions as it helps mitigate risk and increase the likelihood of profitable returns. It allows investors to identify undervalued assets with a higher probability of future growth and reduce the risk of investing in overvalued assets that may experience a decline in value.
Calculating the Margin of Safety
There are several methods for calculating the margin of safety:
- Discounted Cash Flow Analysis (DCF):Projects future cash flows of an asset and discounts them back to the present to determine its intrinsic value.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio:Compares the current market price of a stock to its annual earnings per share.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio:Compares the current market price of a stock to its book value, which represents the value of its assets minus its liabilities.
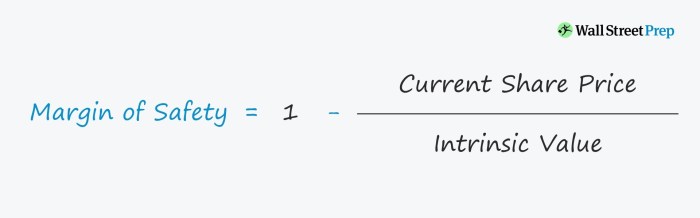
Once the intrinsic value is determined, the margin of safety can be calculated as follows:
Margin of Safety = (Intrinsic Value
Market Price) / Market Price
Factors Affecting the Margin of Safety
The margin of safety can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Market Sentiment:Positive market sentiment can lead to overvalued assets, reducing the margin of safety.
- Interest Rates:Changes in interest rates can affect the intrinsic value of assets, particularly those with long-term cash flows.
- Economic Conditions:Economic downturns can reduce the intrinsic value of assets, decreasing the margin of safety.
- Competition:Increased competition can reduce the profitability and intrinsic value of a business, impacting the margin of safety.
- Management Quality:Effective management can enhance the intrinsic value of a company, increasing the margin of safety.
Applying the Margin of Safety in Investment Decisions, The margin of safety is check all that apply
The margin of safety can be used to identify undervalued investments and make more informed decisions:
- Identifying Undervalued Assets:Investors can seek assets with a margin of safety greater than a predefined threshold, indicating potential undervaluation.
- Setting Target Prices:The margin of safety can be used to determine a target price for an asset, providing a benchmark for buying and selling decisions.
- Reducing Risk:Investing in assets with a margin of safety reduces the risk of permanent capital loss, as there is a buffer against potential declines in market value.
Limitations of the Margin of Safety
While the margin of safety is a valuable tool, it has certain limitations:
- Subjectivity:Determining the intrinsic value of an asset can be subjective, leading to variations in the calculated margin of safety.
- Market Inefficiency:The margin of safety assumes that the market is inefficient, which may not always be the case.
- Unpredictable Events:The margin of safety does not account for unpredictable events, such as natural disasters or economic crises, which can significantly impact asset values.
Detailed FAQs: The Margin Of Safety Is Check All That Apply
What is the purpose of the margin of safety?
The margin of safety is designed to provide a buffer against potential losses and increase the likelihood of achieving positive returns.
How do I calculate the margin of safety?
There are several methods for calculating the margin of safety, including using financial metrics such as the price-to-earnings ratio, the price-to-book ratio, and the discounted cash flow model.
What factors can affect the margin of safety?
The margin of safety can be affected by factors such as the industry, the company’s financial health, and the overall market conditions.