Comparing plant and animal cells venn diagram answer key – Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the captivating realm of plant and animal cells, their intricate structures, diverse functions, and the fascinating processes that govern their lives. Through the lens of a comprehensive Venn diagram, we will unravel the similarities and differences that define these fundamental units of life.
As we explore the depths of cell biology, we will uncover the remarkable adaptations that enable plant cells to harness the power of photosynthesis, while animal cells excel in cellular respiration. We will delve into the intricacies of cell division, tracing the delicate dance of mitosis and meiosis as they orchestrate the creation of new cells.
Cell Structure
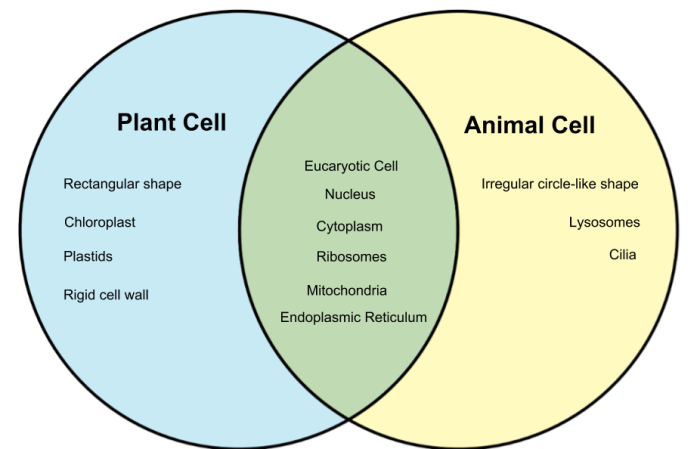
Plant and animal cells are the basic unit of life for all living organisms. They share many similarities in their structure, but they also have some unique features that distinguish them from each other.
Both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains all of the cell’s organelles.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material.
Plant cells have a few unique features that animal cells do not have. These include a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support and protection.
Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. The large central vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that contains water, salts, and other molecules.
Animal cells have a few unique features that plant cells do not have. These include centrioles and lysosomes. Centrioles are small, cylindrical organelles that help to organize the cell’s microtubules. Lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes that break down waste products and cellular debris.
Cell Function
Plant and animal cells have different functions that are related to their different structures. Plant cells are primarily responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert sunlight into glucose. Animal cells are primarily responsible for heterotrophic nutrition, the process by which they obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
The different organelles in plant and animal cells contribute to the overall function of each cell type. For example, chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis, while mitochondria in animal cells are responsible for cellular respiration.
Cell Reproduction
Plant and animal cells reproduce by cell division. Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two new cells. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Mitosis is used for growth and repair of tissues.
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis is used for sexual reproduction.
Cell Organization
| Cell Type | Cell Wall | Chloroplasts | Centrioles | Nucleus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Animal | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Cell Communication
Plant and animal cells communicate with each other through a variety of mechanisms. These mechanisms include direct contact, chemical signals, and electrical signals.
Direct contact is the most direct way for cells to communicate with each other. When cells are in close contact, they can exchange molecules and ions through their cell membranes.
Chemical signals are another way for cells to communicate with each other. Chemical signals are molecules that are released by one cell and received by another cell. Chemical signals can be used to send a variety of messages, such as signals that trigger growth, differentiation, or apoptosis.
Electrical signals are another way for cells to communicate with each other. Electrical signals are changes in the electrical potential of a cell membrane. Electrical signals can be used to send a variety of messages, such as signals that trigger muscle contraction or nerve impulses.
Cell Differentiation, Comparing plant and animal cells venn diagram answer key
Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in their function. Cell differentiation is a complex process that is controlled by a variety of genes.
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that can give rise to any type of cell in the body. Stem cells are found in the embryo and in some adult tissues.
As stem cells divide, they become more specialized. The daughter cells of stem cells are called progenitor cells. Progenitor cells are more specialized than stem cells, but they can still give rise to a variety of cell types.
As progenitor cells divide, they become even more specialized. The daughter cells of progenitor cells are called differentiated cells. Differentiated cells are specialized in their function and cannot give rise to other cell types.
Query Resolution: Comparing Plant And Animal Cells Venn Diagram Answer Key
What is the primary difference between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells possess a rigid cell wall and chloroplasts for photosynthesis, while animal cells lack these structures.
How do plant cells convert sunlight into energy?
Chloroplasts, organelles found exclusively in plant cells, harness sunlight through photosynthesis to produce glucose.
What is the role of centrioles in animal cells?
Centrioles are involved in organizing microtubules during cell division.